A fracture can be a scary experience—for both kids and their parents. But the good news? Children’s bones have an incredible ability to heal quickly and often more completely than adults'. Still, it’s natural to have questions about what recovery looks like and how to support your child along the way.
In this guide, we’ll break down what happens after a fracture, what the healing timeline typically looks like, and how to spot signs that something may not be healing properly. Whether your child has a broken wrist from the playground or a sports-related injury, knowing what to expect can give you peace of mind and help your child heal stronger.
Understanding Pediatric Fractures: What Parents Need to Know
Pediatric fractures differ greatly from adult fractures. Children's bones are softer and more flexible, allowing for quicker recovery.
Parents should know the types of fractures their children may experience. Various types affect kids differently. Proper care ensures your child recovers effectively.
Difference Between Fracture and Break: Clearing Up the Confusion
Many people use "fracture" and "break" interchangeably. They both mean a bone has a crack or a break.
Here's a simple list to clarify:
- Fracture: Medical term for any break in the bone.
- Break: Common term, synonymous with fracture.
Common Types of Pediatric Fractures
Pediatric fractures occur in various forms, each with distinct features. Children’s bones have unique characteristics, making some fracture types more prevalent.
Understanding these types can help in their prompt identification and treatment. The following are common pediatric fracture types:
- Greenstick Fractures: Bones bend and crack instead of breaking completely.
- Buckle (Torus) Fractures: One side of the bone compresses, creating a raised buckle.
- Growth Plate Fractures: Occur at the growth plate, affecting bone development.
Each fracture type requires specific attention to ensure proper healing. Greenstick and buckle fractures often result from falls or minor impacts.
Growth plate fractures, however, need special care due to their potential impact on future growth. Recognizing these differences is essential for parents and caregivers to advocate for proper care.
Causes and Risk Factors for Fractures in Children
Fractures in children often result from their active nature. Young children are naturally curious and engage in physical play.
Common causes include:
- Falls from playground equipment
- Sports-related injuries
- Household accidents
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of fractures. Children involved in high-impact sports face a greater risk.
A lack of supervision or safety measures at home also contributes. Ensuring a safe environment and proper protective gear can mitigate these risks. By addressing these factors, parents can better protect their children's bone health.
Recognizing a Fracture: Signs and Symptoms
Identifying a fracture in your child can seem challenging. However, there are clear indicators to look out for.
Common signs include:
- Swelling or bruising around the injury
- Persistent pain, worsening with movement
- An obvious deformity in the limb's appearance
If your child cannot move the affected area, it may suggest a fracture. Noticing these signs early is vital for timely treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional to confirm and address any concerns regarding potential fractures.
Diagnosing Pediatric Fractures: What to Expect
When you visit a healthcare provider, they'll assess the injury thoroughly.
Imaging helps clarify the fracture type and severity. This information guides the treatment plan. Proper diagnosis ensures your child gets the right care for optimal healing. The process is quick and non-invasive, easing your child's discomfort.
The Healing Process: Stages of Bone Repair in Children
Healing starts immediately after a fracture occurs.
The initial stage, known as inflammation, begins with swelling and pain. This phase prepares the area for healing.
Next, bone production occurs. A soft callus forms around the fracture. This callus eventually hardens, providing necessary support.
The final stage is bone remodeling. During this phase, the callus reshapes into normal bone structure. This process restores the bone to its original state.
Children's bones heal faster due to their unique biological characteristics. Their thicker periosteum and increased flexibility accelerate recovery. This efficient healing process is critical for timely recovery. It highlights the resilience of children's growing bodies.
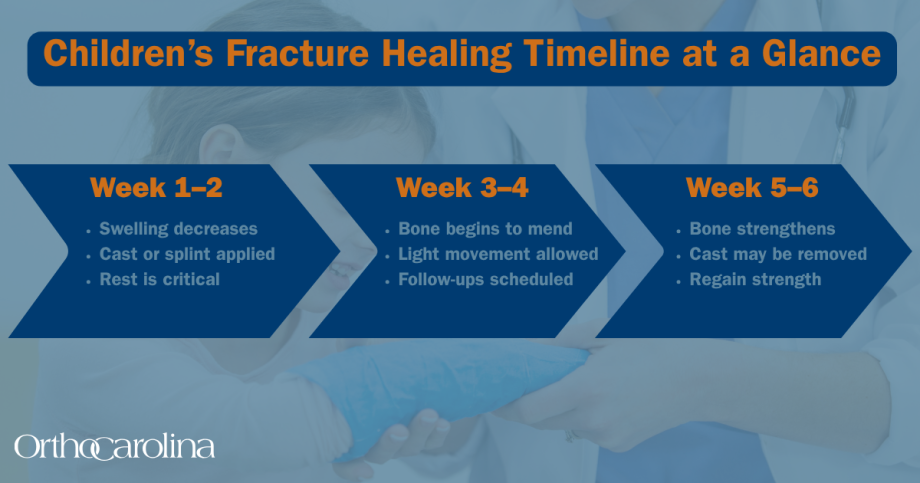
Timeline for Healing: How Long Do Fractures Take to Heal in Children?
Children's bones typically heal quicker than adults'.
On average, simple fractures may heal within three to six weeks. However, the specific timeline can vary based on several factors.
Key factors influencing healing time include:
- Age of the child: Younger children often heal faster.
- Type of fracture: Complexity can extend recovery.
- Bone involved: Larger bones might take longer to mend.
Complex fractures may prolong healing. Continued medical supervision ensures optimal recovery. Ensuring proper care and follow-up is crucial for successful outcomes.
Treatment Options: Casts, Splints, and Surgery
Treating fractures in children often begins with immobilization. Casts and splints are common tools used by specialists.
Casts provide rigid support, keeping bones in place. They are ideal for many stable fractures.
Splints, on the other hand, allow some flexibility and are usually used for minor injuries. Splints are often utilized initially before swelling decreases.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary. This usually occurs with fractures that are complex or if alignment issues exist.
Each treatment is tailored to the child's specific needs. An orthopedic specialist determines the best approach, ensuring effective healing and minimal discomfort.
Growth Plate Fractures: Special Considerations
Growth plate fractures require close attention. These fractures occur where children's bones grow, impacting future development.
Such fractures can potentially affect bone growth. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical to ensure proper healing and prevent complications.
Signs a Broken Bone Is Not Healing: When to Seek Help
Identifying issues early aids in effective treatment. Persistent pain or swelling may indicate that healing isn't occurring properly.
Symptoms that signal problems include:
- Ongoing swelling: Doesn't diminish over time.
- Unrelenting pain: Persists despite rest.
- Limited mobility: Continues beyond expected recovery.
If these symptoms arise, contacting a healthcare professional promptly is crucial. They can assess and address any complications, ensuring the bone heals correctly. Regular follow-up appointments help monitor progress and catch issues early.
Supporting Your Child’s Recovery: Nutrition, Activity, and Emotional Care
A child's recovery journey involves more than just physical healing. Nutrition plays a vital role in strengthening bones. Ensure your child gets enough calcium and vitamin D for optimal bone health.
Balanced activity keeps the recovery smooth. Light movement, as advised by healthcare providers, is crucial once the fracture allows. This prevents muscle stiffness and promotes circulation.
Emotional well-being should not be overlooked. Offer comfort and understanding to support your child through recovery. Listen to their feelings, and provide reassurance to help ease any anxiety about healing.
Preventing Future Fractures: Tips for Parents and Caregivers
Preventing fractures in children is vital for their well-being. Awareness and precaution can significantly reduce injury risks.
Parents and caregivers can enhance safety by considering the following actions:
- Encourage protective gear for sports activities
- Implement childproof measures at home
- Ensure a balanced diet with calcium and vitamin D
Innovative Treatments and Research in Pediatric Orthopedics
Pediatric orthopedics is advancing at a remarkable pace, focusing on improving fracture care. New techniques are continually developed to enhance recovery.
Current research focuses on:
- Biodegradable implants
- Advanced imaging technologies
- Stem cell therapies
These innovations promise safer and faster bone healing for children, improving long-term outcomes.
The OrthoCarolina Approach: Teamwork, Trust, and Comprehensive Care
At OrthoCarolina, we prioritize a collaborative approach to pediatric fracture care. Our experts work together to ensure each child receives tailored treatment.
Key aspects of our approach include:
- Comprehensive, team-centered care
- Building trust with families
- Ensuring transparency in treatment plans
Trust and mutual respect are our commitments to families.
Empowering Families for Better Bone Health
Healing fractures in children requires informed, compassionate care. By understanding the process, families can play an active role in recovery.
OrthoCarolina is here to support families with expertise and resources. Trust us to guide you towards stronger, healthier futures for your children.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for a child’s fracture to heal?
Most pediatric fractures heal within 3 to 6 weeks, depending on the type and location of the break. Children's bones typically heal faster than adults’ due to their growth rate and bone structure. Your child’s orthopedic specialist will provide a specific timeline based on their injury.
What are signs that a broken bone isn’t healing properly?
Watch for persistent pain, swelling, redness, or difficulty using the affected limb after the initial healing period. These symptoms could indicate delayed healing or a complication and should be evaluated by a pediatric orthopedic specialist.
What can I do at home to support my child’s fracture recovery?
Helping your child rest, following all care instructions from their provider, and keeping any casts or splints dry and clean are key steps. Encourage light movement as approved by the doctor and attend all follow-up appointments to monitor healing. Positive reinforcement and patience can also go a long way in supporting a smooth recovery.
Back




Leave a Comment